Slovenia
Gotovi ste! - You’re finished!
Slovenia has had the sharpest decline in GDP since 2008 of any euro-zone member apart from Greece, although it has so far avoided having to ask for external aid owing to having entered the crisis with a far lower sovereign debt burden. The new Government has indicated that it will continue to avoid a bailout by driving through changes including bank restructuring, privatizations, and pension and labour reforms. However, poverty has increased and many people are no longer able to meet basic needs; without state assistance, the poverty rate is estimated to rise to 24%. Those who can’t find work have dropped out of the labour force. As a result, Slovenia has joined countries where people have taken to the streets to call for a more just and balanced economy, more participatory democracy and the rule of law.
Published on Sat, 2013-07-13 11:36
Slovenia has had the sharpest decline in GDP since 2008 of any euro-zone member apart from Greece, although it has so far avoided having to ask for external aid owing to having entered the crisis with a far lower sovereign debt burden. The new Government has indicated that it will continue to avoid a bailout by driving through changes including bank restructuring, privatizations, and pension and labour reforms. However, poverty has increased and many people are no longer able to meet basic needs; without state assistance, the poverty rate is estimated to rise to 24%. Those who can’t find work have dropped out of the labour force. As a result, Slovenia has joined countries where people have taken to the streets to call for a more just and balanced economy, more participatory democracy and the rule of law. |
|
Published on Mon, 2012-03-19 09:13
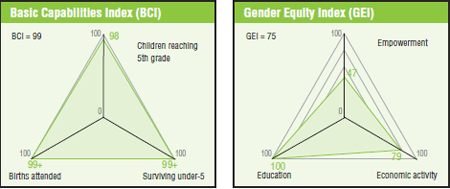
In terms of gender equity Slovenia places itself slightly above the European average and all of its neighbours, but lags far behind the European countries heading the chart. |
SUSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER